Understanding the Physiology of Human Movement
Human movement is a complex and fascinating interplay of biological systems, enabling everything from the subtle gestures of daily life to the powerful, coordinated actions seen in athletic endeavors. Delving into the physiology of human movement provides a deeper appreciation for how our bodies function, adapt, and perform under various conditions. This exploration covers the fundamental mechanisms that drive physical activity and how these systems can be optimized for improved fitness, enhanced performance, and overall well-being. Understanding these intricate processes is key to unlocking our full physical potential and maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle.
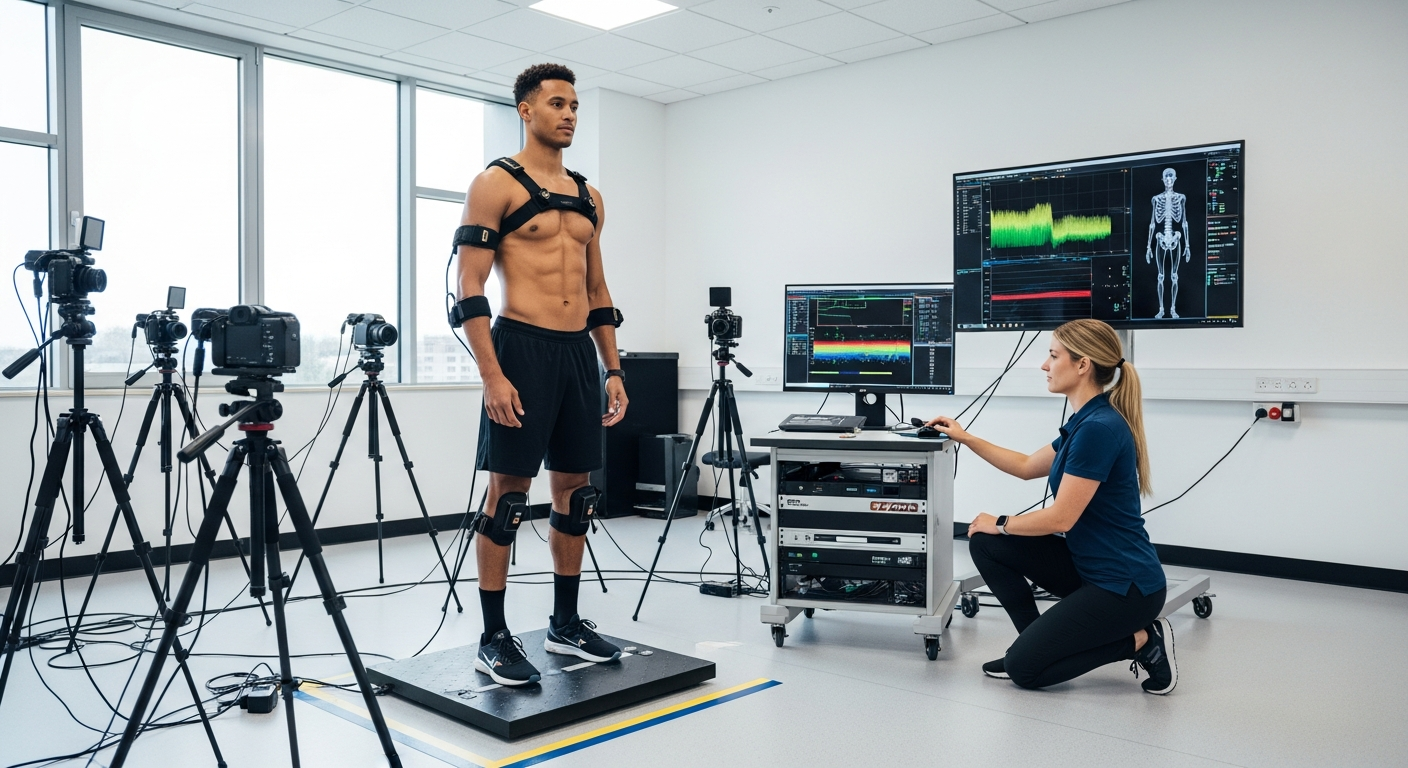
Human movement is fundamentally orchestrated by the nervous, muscular, and skeletal systems working in harmony. The brain sends signals through the nervous system to specific muscles, causing them to contract and generate force. This force, in turn, acts upon the skeletal framework, leading to motion. The efficiency and power of this process depend on factors like muscle fiber type, nerve impulse speed, and joint mechanics. Regular engagement in physical activity, or exercise, stimulates adaptations within these systems, enhancing their capacity for movement and contributing significantly to overall health.
The Foundations of Human Movement and Exercise
At the core of all physical activity lies the intricate physiology of muscle contraction and energy production. Skeletal muscles, categorized into slow-twitch and fast-twitch fibers, are responsible for generating force. Slow-twitch fibers are efficient for prolonged, low-intensity activities, while fast-twitch fibers excel in short, powerful bursts. Energy for muscle contraction is primarily derived from adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is regenerated through various metabolic pathways, including aerobic respiration and anaerobic glycolysis. Understanding these fundamental processes is crucial for comprehending how the body sustains different types of movement and responds to varying exercise demands.
Enhancing Performance Through Training and Conditioning
Optimizing physical performance involves strategic training and conditioning protocols that target specific physiological adaptations. Progressive overload, a key principle of training, gradually increases the demands placed on the body, prompting muscles, cardiovascular systems, and neurological pathways to adapt and become more efficient. This adaptation can manifest as increased muscle mass, improved cardiovascular endurance, or enhanced neuromuscular coordination. Consistent discipline in following a well-structured training regimen is essential for achieving desired improvements in athleticism and overall physical capability, preparing the body for the rigors of competition or personal fitness goals.
Developing Strength, Endurance, and Agility
Strength, endurance, and agility are distinct yet interconnected components of physical fitness, each relying on specific physiological adaptations. Strength training focuses on increasing muscle mass and force production, often through resistance exercises, leading to hypertrophy and improved neural drive. Endurance training, conversely, enhances the cardiovascular and respiratory systems’ ability to deliver oxygen to working muscles, delaying fatigue during prolonged activity. Agility, the ability to change direction quickly and efficiently, involves a combination of strength, coordination, balance, and rapid reaction times. Developing a balanced physique often requires incorporating various forms of exercise to target each of these attributes.
The Role of Movement in Overall Wellness and Health
Regular physical activity is a cornerstone of comprehensive wellness and plays a vital role in maintaining long-term health. Engaging in consistent exercise contributes to cardiovascular health by strengthening the heart and improving blood circulation, reducing the risk of heart disease. It also helps manage body weight, improve bone density, regulate blood sugar levels, and enhance mental well-being by reducing stress and improving mood. Incorporating diverse forms of movement into daily life, whether through structured workouts or recreational activities like sports and play, is essential for fostering a robust and healthy lifestyle.
Physiology in Athleticism and Competition
In the realm of athleticism and competition, understanding human movement physiology becomes critical for optimizing performance and preventing injury. Athletes often undergo specialized training to push the physiological limits of their bodies, focusing on aspects like power output, lactate threshold, and recovery mechanisms. During a game or challenge, the body’s ability to respond rapidly to changing demands, maintain high levels of output, and recover efficiently can be the deciding factor. Sports science applies these physiological insights to develop tailored training programs, nutritional strategies, and recovery protocols that help athletes achieve peak performance and sustain their competitive edge through rigorous conditioning.
Understanding the physiology of human movement offers valuable insights into how our bodies function, adapt, and excel. From the basic mechanics of muscle contraction to the complex adaptations seen in elite athletes, every aspect of physical activity is governed by intricate biological processes. By appreciating these mechanisms, individuals can make informed choices about their fitness routines, enhance their performance, and foster a healthier, more active life, whether through structured training or everyday recreational activity.






